50 to 70 million Americans suffer from a chronic sleep-wake disorder, which interferes with daily functioning and can adversely affect health and longevity. (1)
A good night’s sleep is necessary for good physical and mental health and a good quality of life. Insufficient sleep is a modern and prominent problem in society today. Our production of melatonin (sleep hormone) is disrupted by stimuli, screens and blue light and food. A significant amount of evidence suggests that insufficient sleep causes many adverse medical and mental disorders.
We look at how red light therapy can restore the biorhythm, bring the body back into balance and optimize cellular functions.
What is Melatonin?
Melatonin, often referred to as the sleep hormone, is a central part of the body’s sleep cycle. The body naturally produces melatonin, by the pineal gland in the brain, at nightfall, to prepare the body for sleep. So its production increases as it gets dark. Melatonin promotes a good night’s sleep and helps to orientate our biorhythm.
What Causes Sleep Deprivation?
Globally, insufficient sleep is common among different age groups. This is considered a public health epidemic that is often unrecognized, underreported and has a fairly high economic cost.
Nutrition: What you eat can affect your sleep. Spicy food, caffeine, theine, alcohol, … also eating too late at night can possibly be triggers for people with sleeping problems. Food stays in our system long after it has passed the mouth. This can provide energy or keep your metabolism going, which can lead to a less good night’s sleep.
Lack of exercise: Sleep and exercise complement each other. Exercising regularly can help you sleep better, and conversely, exercising is more likely to get you a good night’s sleep.
Mental state: Depression, listlessness and an active brain during the night. This could also be due to S.A.D. (seasonal mood disorder) and it is due to a lack of sufficient natural light.
Blue light/screen biorhythm disruption: The increased use of smartphones and electronic devices can disrupt human biorhythms. (2)
Humans are programmed to wake up at sunrise and go to sleep at sunset. This has been the case since the dawn of man. People are therefore adjusted to this that our body prepares us for a good night’s sleep before going to sleep. To do this, the body produces melatonin. Research shows that the production of melatonin is related to light. (3)
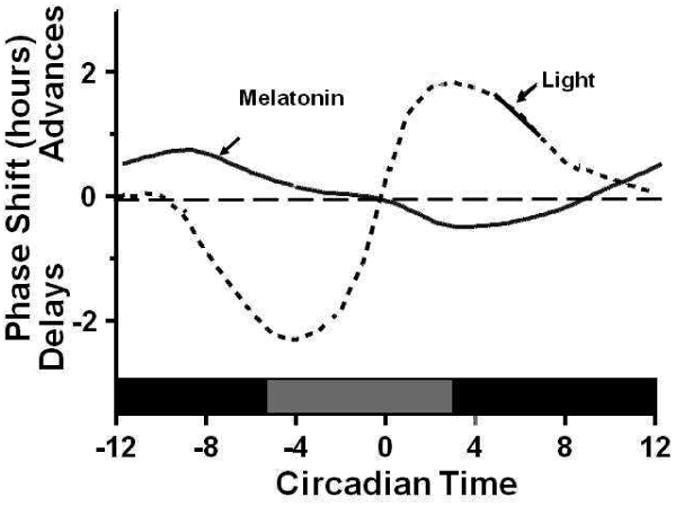
Schematic representation of the phase response curves to light and melatonin(4)
What are the consequences of sleep deprivation?
Insufficient sleep leads to derailment of body systems, which leads to less alertness, slower reaction time and reduced brain function. This can lead to increased incidence, car accidents and more workplace accidents. (2)
In the longer term, ignoring sleep problems and disturbances can lead to weight gain, cardiovascular morbidity, increased risk of diabetes mellitus, obesity, cognitive impairment, accidents, decreased work performance, memory problems and hypersensitivity, strained relationships. (3) If you want to feel your best, stay healthy and perform at your best, good sleep is a necessity, not a luxury.
Red light therapy for sleep, melatonin, and biological rhythm.
Remarkable advances have been made in our understanding of the molecular, cellular and physiological mechanisms underlying human biorhythms, as well as the impact of circadian dysfunction on health and disease. This information has changed our understanding of the effect of circadian rhythm sleep disorders (CRSD) on health, performance and safety. (4)
Clinical studies show that red light therapy can improve sleep quality (6) and length of sleep. Red light therapy can help humans produce more natural melatonin. (5)
Light plays a huge role in the human sleep cycle. The body’s biological clock interprets light as a marker for when it should be asleep or awake. (4)
Artificial blue light from our phones, computers and other screens is extremely bright and can throw our biological clocks off balance. Red light therapy has the opposite effect. It is ideal for the evening because it gives a low color temperature. Much lower than blue light and close to a natural sunset (5)
Red light therapy is not only calming and relaxing, there are also studies showing that it can increase melatonin levels.(7) In addition, it increases your energy during the day by optimizing ATP production, which eliminates many of the side effects of sleep deprivation, such as drowsiness and lack of focus.
Research shows that red light therapy does not disrupt your sleep cycle the way blue light does. On the contrary, red light even shows great results for people with insomnia and sleep disorders. (8)
Sources:
(1) Sleep Disorders and Sleep Deprivation: An Unanswered Public Health Problem
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20669438/
(2) The global problem of insufficient sleep and its serious public health implications
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6473877/
(3) Sleep Disorders in Shift Doctors
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25213642/
(4) Sleep disturbances in the circadian rhythm
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3523094/
(5) Effects of lights of different color temperatures on the nighttime changes in core temperature and melatonin in humans.
http://europepmc.org/article/med/8979406
(6) Red light and the sleep quality and endurance of female basketball players
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23182016/
(7) Aging of Lymphoid Organs: Can Photobiomodulation Reverse Age-Related Thymic Involution by Stimulating Extrapineal Melatonin Synthesis and Bone Marrow Stem Cells
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5995606/
(8) Melatonin as the main component of red light therapy
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17321060/



